Ultimate Guide for Car Audio Subwoofer Enclosures
Get Expert information regarding Subwoofer Enclosures.
Behind every heart-pounding track and every beat that reverberates through your car lies the unsung hero: the subwoofer enclosure. But it’s not just about a box; it’s about the precision, design, and acoustics that transform ordinary drives into extraordinary musical journeys.
As the world of car audio has evolved, so have the complexities and nuances of these enclosures. So, what really differentiates one from another? How do specific materials, intricate designs, and strategic placements converge to create that perfect bass experience on the move?
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll accelerate through the history and engineering of car audio subwoofer enclosures, from classic models to today’s state-of-the-art innovations. For the avid car audio enthusiast looking to fine-tune their setup to the casual listener eager to understand the science behind those pulsating rhythms, this is your essential handbook. So, turn the ignition, adjust your mirrors, and let’s cruise through the captivating world of car audio bass. Your soundtrack to the open road awaits!
Table of Contents
Types of Subwoofer Enclosures:
Different configurations of enclosures are designed to optimize the subwoofer’s performance based on the desired sound characteristics. These types range from fully sealed boxes to complex ported designs.
These are the simplest forms of subwoofer enclosure designs. Their compact nature is due to the air inside the box, which acts as a spring, allowing the subwoofer to move back and forth. Provides tight and punchy bass with a rapid transient response. The bass is accurate, making it suitable for many music genres.
Ported or Vented Enclosures
Distinguished by the inclusion of a vent or port, which allows air and sound to move freely in and out of the box. They are generally louder than sealed enclosures due to the phase alignment of sound waves from the port and the subwoofer itself. This design is particularly effective for producing deep bass notes. The bass might not be as tight or accurate as sealed boxes. Design and tuning of the port are critical for optimal performance.
Bandpass Enclosures
This is essentially a combination of sealed and ported designs. The subwoofer is housed between two chambers – one sealed and one ported. Known for producing a significant bass boost within a specific frequency range. When designed correctly, they can deliver incredibly loud bass from specific narrow frequency bands. Outside of their optimized frequency range, they may not perform as efficiently. They can also be larger and more complex to design and build.
Free-Air or Infinite Baffle Enclosures
A unique design where the subwoofer is mounted directly to a board or baffle with no traditional enclosure. The space behind this board, often the car’s trunk, acts as the enclosure. These systems save space and can utilize existing structures (like the rear deck of a car). They also generally require less power than other designs. It may not provide the deepest bass response. The size and shape of the trunk or space behind the baffle can also influence the quality of the bass.
Transmission Line Enclosures
A more intricate design, the internal structure of these enclosures is built as a labyrinth or tunnel which guides the sound waves from the rear of the subwoofer to an output vent or terminus. Offers a deeper bass extension and can reduce distortion due to the sound wave’s extended path. It provides a smooth and extended low-frequency response.
Materials Used in Enclosures:
The various substances and materials used to construct the enclosure were chosen for their acoustic properties, durability, and ease of working with.
Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF)
A dense wood composite material, it is ideal for subwoofer boxes due to its strength and resistance to resonant vibrations.
Plywood
A layered wood material, sturdy and often used for custom enclosure designs. It’s durable but might not be as acoustically neutral as MDF.
Particle Board
Made from wood particles and adhesive, it’s less expensive but not as strong or dense as MDF, making it less commonly used for subwoofer enclosures.
Fiberglass
A lightweight and moldable material often used for custom and irregularly shaped enclosures, especially in tight spaces like car interiors.
Acrylic or Plexiglass
Transparent materials are often used for aesthetic purposes, allowing viewers to see inside the enclosure. They are typically combined with other materials for structural integrity
Acoustic Properties:
The sound characteristics and behaviors of an enclosure, including how it resonates, dampens sound waves and affects the overall audio output.
Resonance
The natural frequency of a subwoofer enclosure refers to the specific vibrational frequency at which the enclosure itself tends to resonate. This is a critical aspect in the design of subwoofer enclosures. Ideally, the natural frequencies of the enclosure should be higher than the frequencies produced by the subwoofer. This design consideration ensures that the enclosure does not resonate in sympathy with the subwoofer’s output, which can lead to distorted sound quality or even damage to the subwoofer.
Damping
The reduction of resonance within a subwoofer enclosure is a critical aspect of its design. This process involves minimizing the enclosure’s natural tendency to vibrate at certain frequencies. The goal is to prevent these vibrations from interfering with the sound produced by the subwoofer. When a subwoofer enclosure resonates, it can create additional sound waves that mix with those produced by the subwoofer itself, leading to sound distortion. By reducing this resonance, the enclosure ensures that the bass output remains clear and undistorted.
Sound Pressure Level (SPL)
A measure of the loudness or efficiency of a subwoofer in its enclosure. Higher SPL means the subwoofer can produce louder sounds with the same amount of power.
Frequency Response
The range of frequencies a subwoofer can reproduce within its enclosure. A more comprehensive range indicates more accurate bass reproduction.
Phase Response
How the movement of the subwoofer diaphragm corresponds to its input signal within the enclosure. An incorrect phase can lead to bass notes canceling each other out.
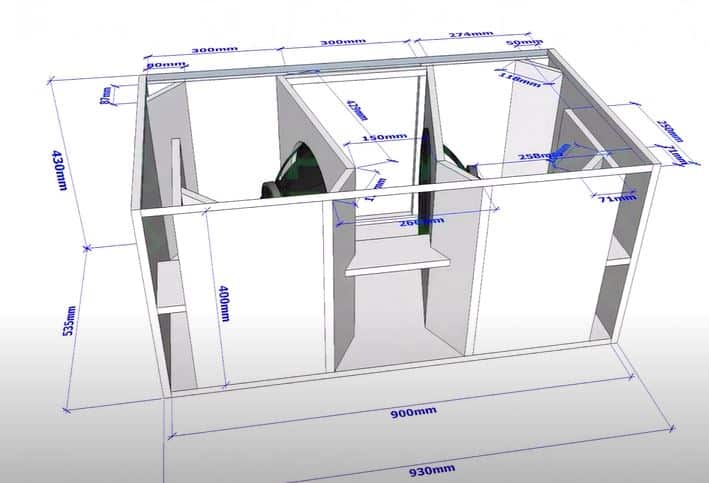
Design and Dimensions:
The physical aspects of the enclosure include its size, shape, and internal components. These factors are crucial in determining the subwoofer’s sound quality and performance.
Box Volume
The internal space within the enclosure. It’s crucial for determining how freely the subwoofer can move and thus its bass output.
Port Length and Diameter
In ported designs, these dimensions determine the tuning frequency of the enclosure and affect the type and quality of bass produced.
Box Shape
The form of the enclosure can influence its acoustic properties and how it fits within a given space.
Internal Bracing
Structural supports within the enclosure reinforce its walls, reducing vibrations and ensuring sound clarity.
Subwoofer Displacement
The subwoofer takes up the volume within the enclosure. It must be accounted for to ensure accurate internal volume.
Tuning Frequency:
Refers to the specific frequency a ported subwoofer enclosure is designed to resonate. Proper tuning can enhance bass response and reduce distortion.
Ported Box Tuning
The specific frequency at which a ported enclosure is optimized. It determines the type of bass the box will produce most efficiently.
Bandpass Box Tuning
In bandpass designs, this is the frequency where the bass output will be maximized, often at the expense of a narrower frequency range.
Effects on Low-Frequency Extension
How the tuning frequency can influence the lowest frequencies the subwoofer can reproduce.
Effects on Group Delay
The time difference between the input signal and the sound produced by the subwoofer. Tuning can affect this delay, potentially leading to “muddy” bass.
Resonant Frequency
The natural frequency at which the subwoofer vibrates. The box tuning should avoid this frequency to prevent unwanted peaks in bass response.
Installation & Positioning:
Guidelines and best practices for placing and securing the subwoofer enclosure in a vehicle or room to achieve optimal sound performance.
Vehicle Trunk Placement
Installing the subwoofer enclosure in the trunk space. This is the most common placement in cars, maximizing bass resonance while preserving cabin space.
Under-Seat Placement
Positioning the subwoofer enclosure beneath the seats, especially in vehicles with limited trunk space. It’s more discreet but might compromise on bass output.
Rear Shelf Placement
Installing the subwoofer on the rear shelf of the vehicle, behind the back seats. It offers a balance between bass output and space-saving.
Custom Installations
Unique, often professionally designed installations tailored to a vehicle or space, maximizing both aesthetics and sound quality.
Angle & Direction
Refers to the orientation of the subwoofer to the listener. Adjusting this can influence how sound waves interact and are perceived.
Subwoofer Matching:
Ensuring that a subwoofer and its enclosure are compatible regarding power, impedance, and other technical specifications.
Power Handling
Ensuring the subwoofer’s capacity to handle the amplifier’s output power without distortion or damage.
Impedance Matching
Aligning the resistance of the subwoofer with that of the amplifier for optimal power transfer and performance.
Sensitivity
A measure of the subwoofer’s efficiency in converting power into sound. Matching sensitivity ensures consistent sound levels across audio components.
Recommended Box Size
The manufacturer’s recommended enclosure volume for optimal subwoofer performance.
Voice Coil Configuration
Refers to the design and number of voice coils in the subwoofer. Matching this with the amplifier affects power handling and impedance.
Acoustic Measurement Tools:
Devices and software used to measure and analyze the sound output of a subwoofer enclosure, helping in tuning and optimization.
RTA (Real-Time Analyzers)
Devices that provide a visual representation of the frequency spectrum, helping in tuning and identifying problem frequencies.SPL Meters
Instruments that measure the loudness or sound pressure level of the audio output are helpful for calibrating systems.Port Velocity Meters
Tools that measure the speed of air moving through a ported enclosure’s vent, ensuring it’s within safe limits.Microphones
Used to capture sound for analysis, especially in tuning and system calibration setups.Software Solutions
Digital applications and programs are used to analyze, tune, and optimize the audio output of subwoofer enclosures.
Aesthetic Design:
The visual and decorative aspects of the enclosure, including its finish, lighting, and other design elements, enhance its appearance.
Carpeting & Vinyl Wraps
Materials used to cover the exterior of the enclosure, not only for aesthetics but also for protection and durability. They come in various colors and textures to match vehicle interiors or personal preferences.
LED Lighting
Decorative lighting components can be installed within or around the enclosure to give it a modern, stylish look, especially in custom car audio setups.
Plexiglass Windows
Transparent sections in the enclosure, allowing viewers to see the subwoofer and internal components. It adds a visual appeal and can showcase the craftsmanship of custom builds.
Custom Paint & Graphics
Personalized paint jobs or designs on the enclosure reflect the owner’s style or the theme of the vehicle/audio setup.
Embellishments & Logos
Additions like brand logos, badges, or other decorative elements enhance the enclosure’s appearance and indicate brand allegiance or quality.
Advanced Enclosure Designs:
More complex and specialized enclosure configurations that use unique principles to produce specific sound characteristics.
Quarter Wave Designs
Enclosures are designed around the principle of quarter-wavelength resonance, providing deep bass extension and unique sound characteristics.Horn-Loaded Designs
It utilizes a horn shape to amplify the sound, increasing efficiency and SPL.Tapped Horn Designs
A variation of the horn-loaded design where the subwoofer is placed inside the horn pathway, optimizing bass response.Passive Radiator Designs
It uses a secondary, non-powered diaphragm (passive radiator) to augment the bass response, especially in smaller enclosures.Iso-Baric Configurations
It incorporates two subwoofers operating in tandem within the same enclosure, producing deeper bass from a compact size.
Acoustic Enhancements:
Electronic and mechanical adjustments and additions can be made to improve the sound quality or characteristics of the subwoofer output.
Bass Boost Circuits
Electronic circuits that amplify specific low-frequency ranges, enhancing the perceived bass response.Parametric Equalizers
Allows for precise adjustments of specific frequency bands, enabling detailed tuning of the sound output.Phase Controllers
Devices that adjust the phase alignment between the subwoofer and other speakers, ensuring cohesive sound reproduction.Crossovers
Electronic filters that direct specific frequency ranges to the subwoofer, ensuring it only reproduces suitable bass frequencies.Time Alignment
Adjusts the timing of sound waves from multiple speakers, ensuring they reach the listener simultaneously for a unified soundstage.
Maintenance & Troubleshooting:
Tips and solutions for addressing common issues with subwoofer enclosures and ensuring long-term performance.
Rattling & Vibrations
Addressing unwanted noises often caused by loose parts or internal resonances in the enclosure.Port Noise & Chuffing
Resolving noises from air turbulence in ported enclosures which can be due to high volumes or incorrect port design.Wear & Tear
Regular maintenance checks for physical damages, worn-out components, or other signs of aging in the enclosure and subwoofer.Re-sealing Joints
Ensuring the enclosure remains airtight, especially in sealed designs, to maintain optimal performance.Subwoofer Failures
Diagnosing and addressing issues where the subwoofer stops functioning or performs below par, often due to electrical or mechanical failures.
Environmental Impact:
Considerations regarding the effect of the subwoofer and its enclosure on its surroundings, including power consumption, heat production, and long–lasting effects on the environment
Impact on Vehicle’s Electrical System
Considerations for the additional power drawn by the subwoofer and its potential effects on a car’s battery and alternator.Fuel Efficiency
Understanding how the added weight and power consumption of a subwoofer system can influence a vehicle’s fuel economy.Weight Considerations
The influence of the subwoofer and enclosure’s weight on vehicle performance, especially in suspension and braking.Heat Dissipation
Ensuring the subwoofer and its amplifier remain cool during operation, preventing overheating and potential damage.Long-Term Durability
Factors affecting the lifespan of the subwoofer and enclosure, including material quality, usage habits, and environmental conditions.